PART 3 – TECHNICAL ANALYSIS
Risk management is an essential skill that every trader must master to ensure long-term profitability and capital preservation. Without proper risk management, even the best trading strategies can lead to significant losses. In this blog, we will explore crucial risk management techniques derived from professional trading methodologies.
Trading on Different Time Frames
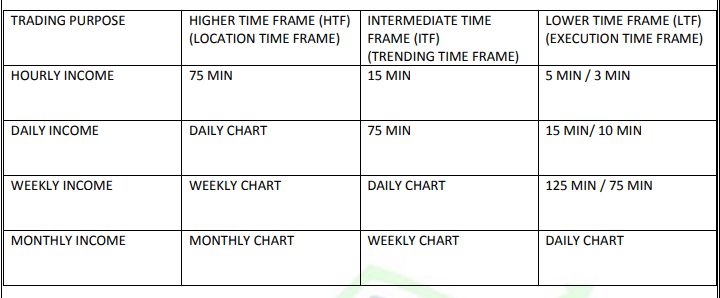
Curve Analysis
- It is also known as location analysis.
- What is location???
- Location gives you an idea about how high or how low you are on theprice curve.
CAUTION :
- If you are buying on a strong daily demand but you are near weeklysupply, Chances are very high that your
will get stopped out. - If you are selling on strong 15 min supply, but you are near to daily demand, chances are very high that your
trade will getstopped out.
Steps in Identifying location on a price chart
- Mark Nearest fresh supply zone & nearest fresh Demand zone.
- Divide this area between supply and demand into 3 parts by using
retracement tool, start it from proximal line of a supply to proximal line of a demand.

RULES :
- If CMP( Current market price) is trading high on the curve or very high onthe curve.
Action – SELL ( at execution time frame ) - If CMP( Current market price) is trading low on the curve or very low onthe curve.
Action – BUY ( at execution time frame ) - If CMP( Current market price) is trading in an equilibrium area
Action – will go to trending time frame and check the trend and will plantrade according to the trend.
At Intermediate Time Frame
- Trend Up – BUY
- Trend Down – SELL
- Trend Sideways – IGNORE
Note –
1.If there is no fresh supply but fresh demand – Assume that stock is trading in the equilibrium and trade with
the trend.
2.If there is no fresh demand but fresh supply – Assume that stock is trading in the equilibrium and trade with
the trend.
Understanding Risk Per Trade
One of the first steps in risk management is determining how much capital to risk per trade. Based on professional guidelines:
- 1% Risk – Suitable for beginners
- 1.5% Risk – Ideal for intermediate traders
- 2% Risk – Used by pro traders
For example, if a trader has a capital of ₹1,00,000 and follows a 1% risk rule, they should not risk more than ₹1,000 per trade. This limits potential losses and allows room for recovery from drawdowns.
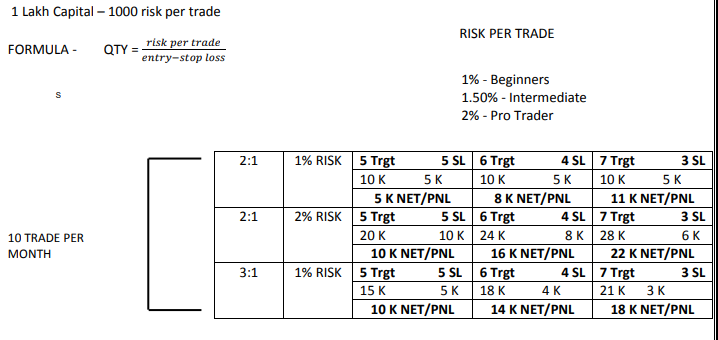
Position Sizing Formula
The right position sizing ensures that traders do not over-leverage their capital. The formula to calculate quantity per trade is:
QTY = Risk per Trade / (Entry Price – Stop Loss Price)
For instance, if the stop-loss distance is ₹10 and the risk per trade is ₹1,000, the position size should be 100 shares.
Risk-to-Reward Ratio
Successful traders ensure that their potential rewards outweigh their risks. The recommended risk-to-reward ratios are:
- 1:2 – A balanced risk-reward setup
- 1:3 – Ideal for sustainable trading
- 1:5 – High-probability trades
If a trader risks ₹1,000, they should aim for a profit of at least ₹2,000 with a 1:2 risk-reward ratio.
Trade Score
A trade’s strength is determined by its score. A minimum trade score of 5 is required for an entry, while a score of 7 or higher is considered ideal.
Components of a Trade Score:
- Freshness
- If a level is fresh: 3 points
- If tested once: 1.5 points
- If tested twice: 0 points
- Strength
- If price leaves the level with a gap: 2 points
- If price leaves the level with two exciting candles: 2 points
- If price leaves the level with only one exciting candle and no gap: 1 point
- Time at the Base
- If the base has 1-3 boring candles: 2 points
- If the base has 4-5 boring candles: 1 point
- If the base has more than 5 boring candles: 0 points

Entry and Exit Strategies
There are three types of entries based on credibility and trade confirmation:
- Set & Forget (Trade Score 7+) – Entry is placed with predefined stop-loss and target, requiring minimal monitoring.
Image: pdf pg20 - Confirmed Entry (Trade Score 5-6) – Entry is made only after price action confirms the trade setup.
Image: pdf pg20 - Aggressive Entry (Trade Score 5+) – Entry is made in anticipation of price action without full confirmation.
Image: pdf pg21 & 22 Multiple cases n multiple images
Exit Strategies
- Target-based exit – Predefined profit target is reached.
- Trailing Stop-Loss – Exit trade as price moves against the trend.
- Break-even Exit – Move stop-loss to entry point when price moves favorably.
Common Trading Mistakes to Avoid
- Overtrading – Taking excessive trades without proper setups.
- Ignoring Stop-Loss – Not using stop-loss increases risk exposure.
- Poor Position Sizing – Trading too large can wipe out capital quickly.
- Emotional Trading – Letting fear and greed dictate decisions.
- Lack of Trade Review – Not analyzing past trades prevents learning.
Conclusion
Risk management is the backbone of successful trading. By implementing proper risk-reward ratios, position sizing, stop-loss strategies, and disciplined trade execution, traders can achieve consistent profitability. Follow these principles and refine your approach to master risk management and thrive in the markets.
Stay tuned for more insights into professional trading strategies!
BUSINESS IDEAS & SIDE HUSTLES
Designed with WordPress

Leave a Reply to Deependra Singh Rathore Cancel reply