The world of finance has long been a source of fascination, drama, and intrigue. From stories of Wall Street excess to the dark side of corporate greed, financial movies offer both education and entertainment. Whether you’re an aspiring investor, an economics enthusiast, or simply looking for an engaging movie night, these 13 films are a must-watch.
1. The Wolf of Wall Street (2013)

Martin Scorsese’s high-octane biographical drama follows Jordan Belfort’s meteoric rise and dramatic fall on Wall Street. With Leonardo DiCaprio’s electrifying performance, this film is an exhilarating watch that showcases the temptations and dangers of financial success.
2. The Big Short (2015)

This Oscar-winning film explains the 2008 financial crisis in an engaging and accessible way. With an ensemble cast, including Christian Bale, Steve Carell, and Ryan Gosling, it unpacks complex financial concepts with humor and sharp storytelling.
3. American Psycho (2000)

While not strictly a financial film, this psychological thriller highlights the materialism and superficiality of Wall Street culture through the chilling story of investment banker Patrick Bateman.
4. Boiler Room (2000)
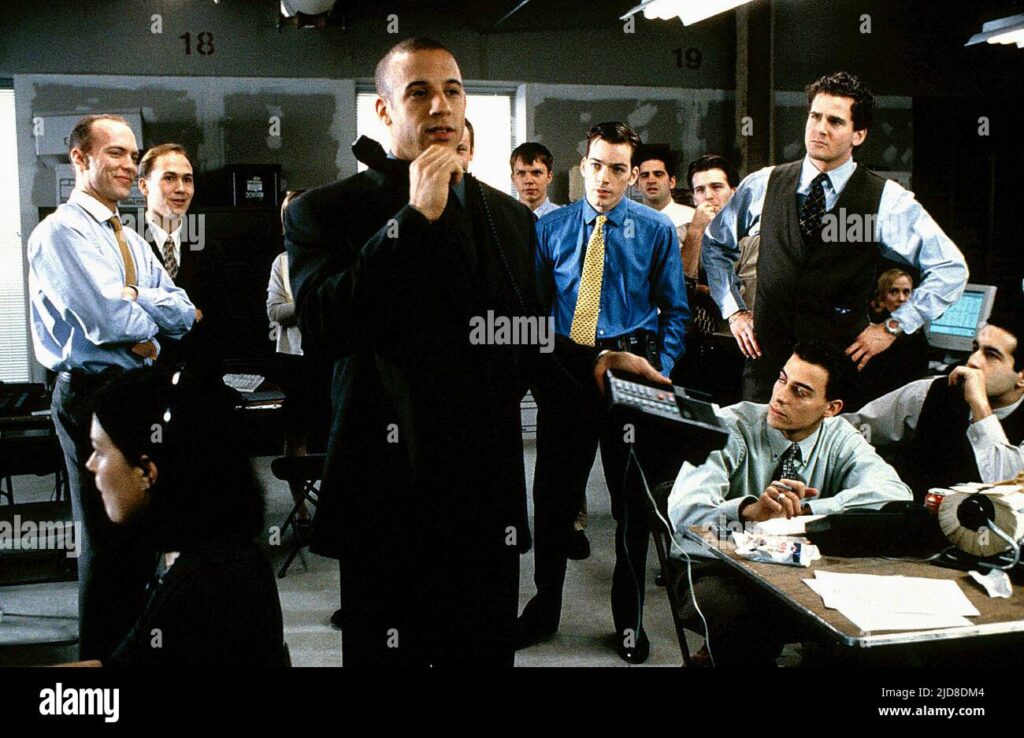

A gripping tale of young stockbrokers enticed by the allure of quick wealth, this film showcases the dark side of aggressive sales tactics and financial fraud.
5. Margin Call (2011)

Set in a 24-hour period at a collapsing investment bank, this intense drama explores the behind-the-scenes decisions that led to the financial meltdown of 2008.
6. Enron (2005)

This documentary unravels one of the biggest corporate frauds in history, exposing the deceptive practices that led to Enron’s downfall.
7. Rogue Trader (1999)

Based on the true story of Nick Leeson, a trader whose reckless decisions led to the collapse of Barings Bank, this film is a cautionary tale about the dangers of unchecked risk-taking.
8. Free Fall (2013 – Short Film)

A lesser-known but powerful short film that explores the emotional and financial toll of an economic crash.
9. Scam 1992: Harshad Mehta Story (2020)

This critically acclaimed Indian web series chronicles the life of Harshad Mehta, the stock market manipulator behind one of India’s biggest financial scams.
10. Inside Job (2010)

An Oscar-winning documentary narrated by Matt Damon, Inside Job provides an in-depth analysis of the 2008 financial crisis and the systemic corruption that led to it.
11. Too Big to Fail (2011)

Based on real events, this film dramatizes the frantic efforts of government officials and financial leaders to prevent the global economy from collapsing in 2008.
12. Wall Street (1987)

Oliver Stone’s classic film, featuring the infamous character Gordon Gekko, remains one of the most iconic portrayals of Wall Street greed and ambition.
13. Betting on Zero (2016)

A compelling documentary that follows hedge fund manager Bill Ackman’s battle against Herbalife, a company accused of being a pyramid scheme.
Honorable Mentions
If you can’t get enough of financial dramas, consider checking out “Barbarians at the Gate” (1993), “The China Hustle” (2017), and “Equity” (2016). These films provide further insights into corporate greed, stock market manipulation, and high-stakes finance.
Conclusion
These movies offer a mix of real-life events, financial scandals, and fictional drama, making them both educational and highly engaging. Whether you’re looking to understand the complexities of the stock market, witness the rise and fall of financial empires, or simply enjoy a well-crafted story, these films have something for everyone.
Which of these movies is your favorite? Let us know in the comments!
BUSINESS IDEAS & SIDE HUSTLES
Designed with WordPress


























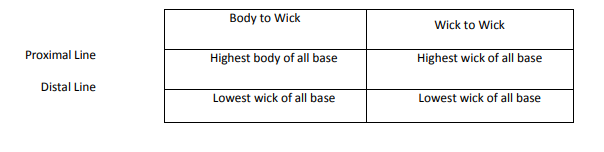
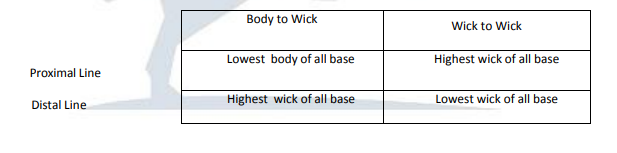
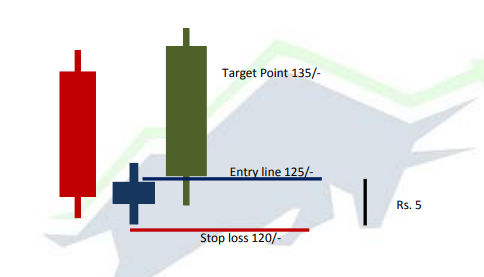
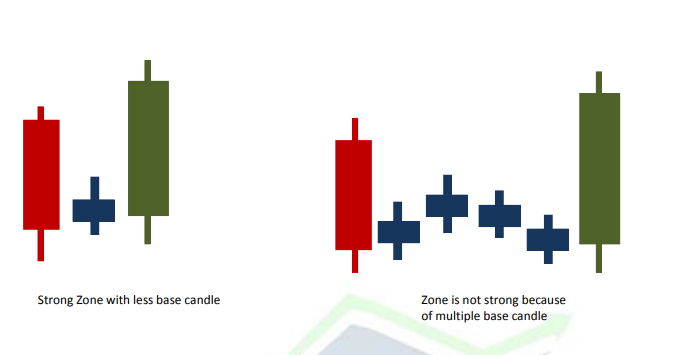


Leave a Reply