PART 7 – TECHNICAL ANALYSIS
Entry and exit strategies are crucial for profitable trading. A well-planned entry increases the probability of success, while a strategic exit ensures maximum gains and minimal losses. This blog will guide you through professional entry and exit techniques based on demand and supply zones, ensuring you make informed trading decisions.
Understanding Trade Setup
Before entering a trade, it is essential to mark key demand and supply zones. Here’s how:
- Marking the Entry Point:
- Demand Zone Entry: Place the entry just above the proximal line of the demand zone.
- Supply Zone Entry: Place the entry just below the proximal line of the supply zone【92:0†DOC-20240412-WA0000.pdf】.
- Stop-Loss Placement:
- For Buy Trades: Stop-loss should be set just below the distal line of the demand zone.
- For Sell Trades: Stop-loss should be placed just above the distal line of the supply zone【92:1†DOC-20240412-WA0000.pdf】.
- Setting the Target:
- The target is typically set as twice the difference between entry and stop-loss (Risk-to-Reward: 2:1).
- Ensure the trade setup allows for this ratio before execution【92:2†DOC-20240412-WA0000.pdf】.
Entry Strategies
1. Set & Forget Entry (Score 7+)
- Entry is placed with a predefined stop-loss and target, requiring minimal monitoring.
- Suitable for strong demand or supply zones with high credibility【92:6†DOC-20240412-WA0000.pdf】.
2. Confirmed Entry (Score 5-6)
- Wait for price action confirmation before entering a trade.
- Ideal for moderately strong demand/supply zones【92:7†DOC-20240412-WA0000.pdf】.
3. Aggressive Entry (Score 5+)
- Entry is made in anticipation of price movement without full confirmation.
- Used by experienced traders with high risk tolerance【92:8†DOC-20240412-WA0000.pdf】.

Some more Important Entries
- HOW TO TRADE ON SINGLE TIMEFRAME ?
- HOW TO TRADE AGAINST TREND ?
case1:
Image: pdf pg25
case2:
Image: pdf pg25
- IF PRICE COME WITHOUT FORMING SUPPLY ZONE ?
case3 :
Image: pdf pg26
Exit Strategies
1. Target-Based Exit
- Predefined profit target is set at twice the risk amount (2:1).
- Ensures disciplined profit booking【92:9†DOC-20240412-WA0000.pdf】.
2. Trailing Stop-Loss Exit
- Adjust stop-loss to secure profits as price moves in favor.
- Best for trend-following trades to maximize gains【92:10†DOC-20240412-WA0000.pdf】.
3. Break-Even Exit
- Stop-loss is moved to the entry point when price moves favorably.
- Used to minimize risk and protect capital【92:11†DOC-20240412-WA0000.pdf】.
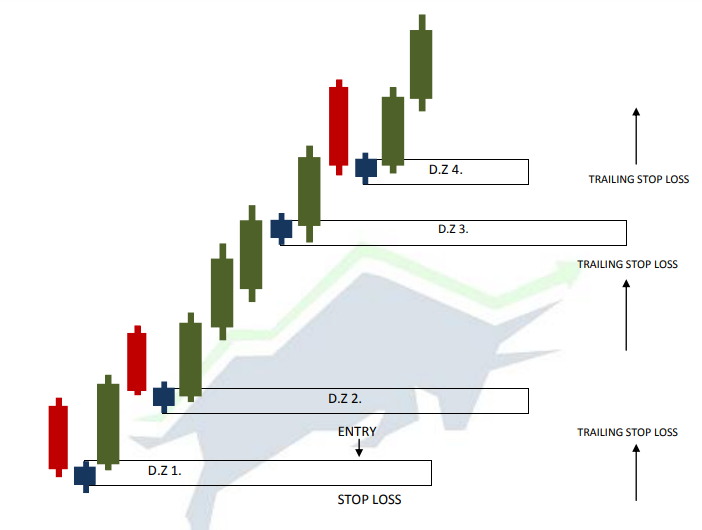
Trailing Stop Loss
We do stop loss trailing when the price is on all time high and forming new demand zones.
We shift our stop loss down to the distal line of newly formed demand zone and we will do this until it will get stop loss.
Image: pdf pg40
Trade Management & Psychology
- Follow Your Plan: Stick to your strategy and avoid emotional trading.
- Avoid Overtrading: Only take high-probability setups with proper risk-reward ratios.
- Journal Your Trades: Keep track of entry and exit decisions for future learning【92:12†DOC-20240412-WA0000.pdf】.
Conclusion
A well-defined entry and exit strategy is key to successful trading. By using demand and supply zones, proper stop-loss placement, and disciplined execution, traders can maximize their profitability and reduce unnecessary risks. Implement these strategies, refine your approach, and trade like a pro!
Stay tuned for more professional trading insights!
BUSINESS IDEAS & SIDE HUSTLES
Designed with WordPress